|
|
|
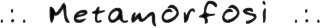
Dido between her handmaids and Africa, Pompeian painting
 Dido between her handmaids and Africa
Pompeian painting
We can divide the Pompeian Painting into four main styles.
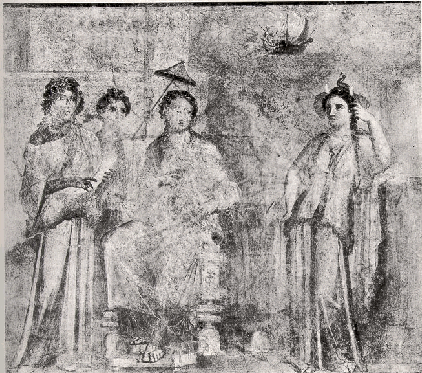
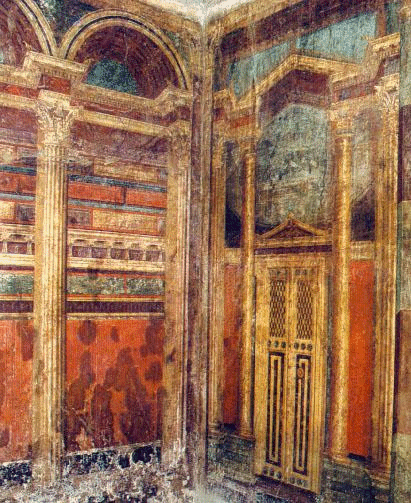
The first technique we find in Pompei goes from about 150 a.C. to 80 a.C.; it consists in an imitation of variegated marble. The dominant colours are black and red with a yellow stripe at the bottom, which produces a contrasting effect with a play of abstract figures. There is also a second type of technique that goes from about 80 a.C. to 10 a.C., characterised by architectonical elements, such as pilasters meant to divide the picture vertically. The painter usually represented an imitation of a stage-scenery. We also have some representations of gardens with lots of flowers and animals such as birds and tropical animals. Tables with dead animals, fruits and vegetables on them were usually painted too. The third technique is chronologically juxtaposed to the second style, in fact it goes from 10 a.C. to 50 A.D. The painters drew on the walls a tenuous architectonical structure, similar to the bamboo; in this structure little scenes with different subjects were inserted, such as landscape and country houses.
The fourth style includes a wide range of different kinds of painting, it goes from 50 A.D. to 85 A.D. We have more paintings belonging to this style than other works belonging to the previous ones. The painters come back to the architectonical features of the second style, and the themes back up to ancient Greek models. In this paintings volumes are widely sketched, faces and feelings are impressionistically Suggested with a few, brave strokes of the brush.
 First style: Sallustio's house
 Second style: villa of misteries
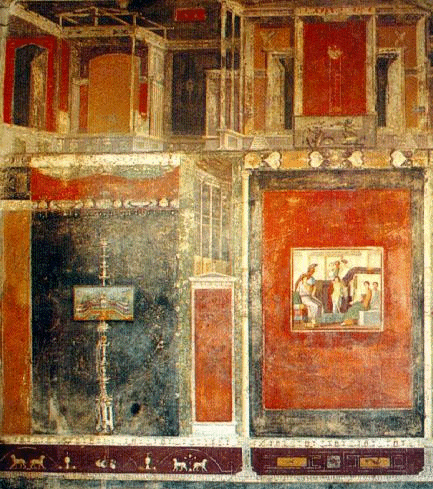 Third style: Lucrezio Frontone's house
 Forth style: Vetii's Villa
|
|