

Sketch of the apparatus

Example of absorption spectrum: oxygen
Second derivative of the molecular oxygen absorption spectrum at ~759 nm along with the inverted transmission of the monochromator centered to the RQ(19) (13160.813 cm-1) line. The measurement has been done at room temperature with an oxygen pressure of 20 Torr, through an optical path length of 3 m and by using a 2.5 ms time constant. [ See A. Lucchesini, M. De Rosa, C. Gabbanini and S. Gozzini, "Diode laser spectroscopy of oxygen electronic band at 760 nm", Nuovo Cimento D 20(3), 253 (1998)]
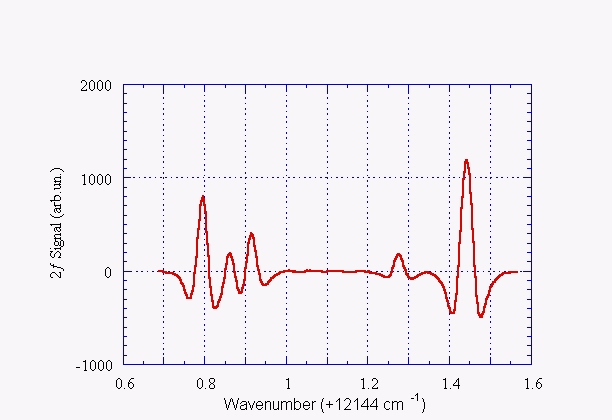
Another example of absorption spectrum: water vapor
Second derivative of the water vapor absorption spectrum at ~823 nm (~13145 cm-1). The measurement has been done at room temperature with a water vapor pressure of 20 Torr, through an optical path length of 5 m and by using a 2.5 ms time constant. The line positions agree with what listed by HITRAN database within 0.01 cm-1: 12144.795, 12144.862, 12144.915, 12145.279 e 12145.444 cm-1 respectively.

Ammonia absorptions at 788 nm
Second derivative of two ammonia absorption lines at 788.8 nm (~12673 cm-1). The measurement has been done at room temperature with 18 Torr of ammonia, through an optical path length of 5 m and by using a time constant of 12.5 ms. Only one line position is well known (12673.72 cm-1). The other differs from this by 0.072 cm-1.
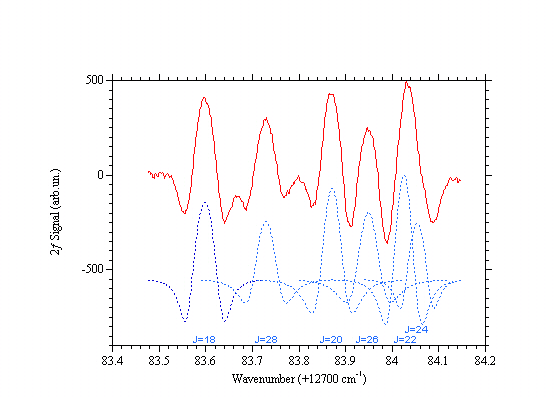
Carbon dioxide absorption lines around 782 nm
Second derivative of the carbon dioxide absorption spectrum at ~782nm. The measurement has been done at room temperature, CO2 pressure = 91 Torr, through 30 m optical path length and 10 Hz bandwidth. This is the R branch at the "turning point". The regression of the value of J is due to the reduction of the constant B as the ro-vibrational energy increases. [ See A. Lucchesini, S. Gozzini, "Diode laser overtone spectroscopy of CO2 at 780 nm", J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 96(2), 289-299 (2005)]Alessandro Lucchesini
CNR - INO
Area Territoriale di Ricerca di Pisa
Via Giuseppe Moruzzi, 1
56124 Pisa - Italy
