Brief History
The eastern portion of Ghana known as the Volta Region, has tended to be regarded by many as having been part of Trans-Volta Togoland which was an integral part of the Republic of Togo. In the past, nearly half the Volta Region, from the coast up to Kpave areas, were part and parcel of the then Gold Coast Colony under the British. Areas from Kpeve upward even up to Yendy in the Northern Region were under the Germans, hence part of the Trans-Volta Togoland. Even though the border often changed in the past, it was assumed that Kpeve was the border between the Gold Coast Colony to the south, and Trans-Volta Togoland to the north. In 1956, after the defeat of the Germans in Second World War, the German Colony was redesignated a Trust Colony under British and French rule. A plebiscite was held to determinate which part of the Trust Colony should belong to the British or French. It emerged that a portion decided to join the Gold Coast while the other portion decided to remain under French rule and become part of Togoland. That portion which decided to join the Gold Coast (now Ghana) became part of the Volta Region of Ghana. The main ethnic groups are Ewes occupying the southern section, the Akans in the northern section and a number of Guan-speaking groups such as Likpe, Nyagbo, Tafi, Logba, Santrokofi, etc. The Guans are supposed be the original dwellers of the land while the Akans migrated from the Ashanti, Brong, Ahafo, Western, Central and Eastern regions. The Ewes migrated from Notsie (in present-day Republic of Togo) centuries ago. All these ethnic groups live within the Volta Region, demonstrating unity and diversity. Introduction The Volta Region is an area of extraordinary scenic beauty, of highly diversified cultural heritage, fascinating landscape of rolling hills and valleys and, above all, the home of a highly ingenious, hardworking and warm people.

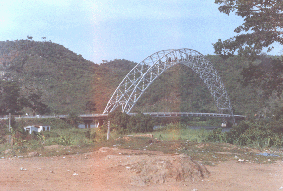
The Adomi Bridge which links the Volta Region with the eastern and southern parts of Ghana
Location
The region is located at the eastern part of Ghana, sharing its eastern border with the Republic of Togo while the western border with the Volta River. The southern border is the Atlantic Ocean, while the north shares a boundary with the Northern Region.
|
a baobab tree |
Volta Region map |
Brief Geography
The region stretches from the shores of the Atlantic Ocean in the south up to the southern fringes of the arid north.
It as three marked climatic and vegetation zones:
The Mangrove Swamps and Adjoining Arid Coastal Plains
This zone is characterised by dense mangrove swamps at the estuarine areas of the Volta River and Keta lagoons. The main vegetable species are the white an red mangroves. The coastal plains are marked by lowsavannah grassland which dries up completely during the dry season. The main tree species are oil palm, silk cotton trees, borassus palm, neem and baobab trees. Mango and coconut palm trees are planted in several areas.
The area has two rainfall maxima:
Between the rainy season is a prolonged dry season, culminating in the dry harmattan -a wind blowing from Sahara Desert- between November and February. Daily temperatures are very high, averaging some 25 °C. Humidity is high averaging 60 %.
The Moist Semi-Deciduous Forest Zone
This zone, occupying the central portion of the region, is made mostly of isolated forests and ahrub-land. The main trees include the silk cotton tree, teak, obeche, wawa, etc. Wild mangos, oil palm and date palm grow in several areas. Most tree shed their leaves during the dry season. The area also experiences the same rainfall patter as the southern zone. The marked difference, however, is the intensity of the rains in the forest zone. Temperature are a few degrees lower than the south, especially in the hill areas. Once again, the humidity is slightly lower.
The Northern Savannah Zone
This zone consists of mostly expansive Savannah grassland, dominated in parts by tall elephant grass. There are a number of wild trees some of which are acacia, baobab, neem and cola trees. The area has one rainfall regime from May to August. The temperatures are slightly higher than in the south. Humidity is, however, slightly lower.
|
a farm near Sogakope |
coastal plains at Ada |