


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Mozambique |

|
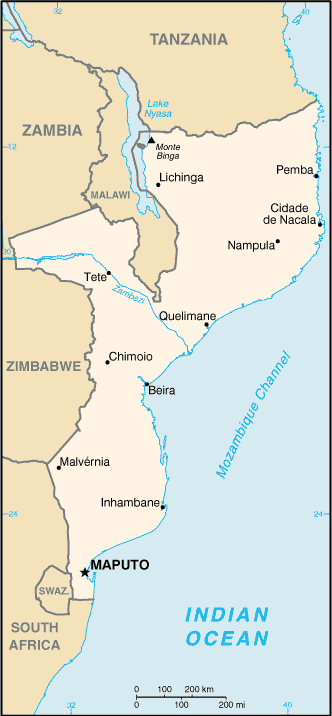
|
| Introduction | Mozambique |
|
Background:
|
Almost five centuries as a Portuguese colony came to a close with independence in 1975. Large-scale emigration by whites, economic dependence on South Africa, a severe drought, and a prolonged civil war hindered the country's development. The ruling Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (FRELIMO) party formally abandoned Marxism in 1989, and a new constitution the following year provided for multiparty elections and a free market economy. A UN-negotiated peace agreement between FRELIMO and rebel Mozambique National Resistance (RENAMO) forces ended the fighting in 1992. In December 2004, Mozambique underwent a delicate transition as Joaquim CHISSANO stepped down after 18 years in office. His newly elected successor, Armando Emilio GUEBUZA, has promised to continue the sound economic policies that have encouraged foreign investment. |
| Geography | Mozambique |
|
Location:
|
South-eastern Africa, bordering the Mozambique Channel, between South Africa and Tanzania |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
18 15 S, 35 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 801,590 sq km
land: 784,090 sq km water: 17,500 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly less than twice the size of California |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 4,571 km
border countries: Malawi 1,569 km, South Africa 491 km, Swaziland 105 km, Tanzania 756 km, Zambia 419 km, Zimbabwe 1,231 km |
|
Coastline:
|
2,470 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
tropical to subtropical |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in northwest, mountains in west |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: Monte Binga 2,436 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
coal, titanium, natural gas, hydropower, tantalum, graphite |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 5.1%
permanent crops: 0.3% other: 94.6% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
1,070 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
severe droughts; devastating cyclones and floods in central and southern provinces |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
a long civil war and recurrent drought in the hinterlands have resulted in increased migration of the population to urban and coastal areas with adverse environmental consequences; desertification; pollution of surface and coastal waters; elephant poaching for ivory is a problem |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
the Zambezi flows through the north-central and most fertile part of the country |
| People | Mozambique |
|
Population:
|
19,406,703
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected; the 1997 Mozambican census reported a population of 16,099,246 (July 2005 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 43.1% (male 4,206,654/female 4,157,898)
15-64 years: 54.1% (male 5,088,250/female 5,416,573) 65 years and over: 2.8% (male 224,682/female 312,646) (2005 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 18.29 years
male: 17.74 years female: 18.83 years (2005 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.48% (2005 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
35.79 births/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
20.99 deaths/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/female total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2005 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 130.79 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 135.91 deaths/1,000 live births female: 125.51 deaths/1,000 live births (2005 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 40.32 years
male: 39.9 years female: 40.75 years (2005 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
4.7 children born/woman (2005 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
12.2% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
1.3 million (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
110,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: malaria and plague are high risks in some locations water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2004) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Mozambican(s)
adjective: Mozambican |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
indigenous tribal groups 99.66% (Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08% |
|
Religions:
|
Catholic 23.8%, Zionist Christian 17.5%, Muslim 17.8%, other 17.8%, none 23.1% (1997 census) |
|
Languages:
|
Emakhuwa 26.1%, Xichangana 11.3%, Portuguese 8.8% (official; spoken by 27% of population as a second language), Elomwe 7.6%, Cisena 6.8%, Echuwabo 5.8%, other Mozambican languages 32%, other foreign languages 0.3%, unspecified 1.3% (1997 census) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 47.8% male: 63.5% female: 32.7% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Mozambique |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Mozambique
conventional short form: Mozambique local long form: Republica de Mocambique local short form: Mocambique former: Portuguese East Africa |
|
Government type:
|
republic |
|
Capital:
|
Maputo |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
10 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia), 1 city (cidade)*; Cabo Delgado, Gaza, Inhambane, Manica, Maputo, Cidade de Maputo*, Nampula, Niassa, Sofala, Tete, Zambezia |
|
Independence:
|
25 June 1975 (from Portugal) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 25 June (1975) |
|
Constitution:
|
30 November 1990 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on Portuguese civil law system and customary law |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Armando GUEBUZA (since 2 February 2005)
head of government: Prime Minister Luisa DIOGO (since 17 February 2004) cabinet: Cabinet elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held 1-2 December 2004 (next to be held December 2009); prime minister appointed by the president election results: Armando GUEBUZA elected president; percent of vote - Armando GUEBUZA 63.7%, Afonso DHLAKAMA 31.7% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral Assembly of the Republic or Assembleia da Republica (250 seats; members are directly elected by popular vote on a secret ballot to serve five-year terms)
elections: last held 1-2 December 2004 (next to be held December 2009) election results: percent of vote by party - Frelimo 62%, Renamo 29.7%; seats by party - Frelimo 160, Renamo 90 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (the court of final appeal; some of its professional judges are appointed by the president and some are elected by the Assembly); other courts include an Administrative Court, customs courts, maritime courts, courts marshal, labor courts
note: although the constitution provides for a separate Constitutional Court, one has never been established; in its absence the Supreme Court reviews constitutional cases |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frente de Liberatacao de Mocambique) or FRELIMO [Armando Emilio GUEBUZA, president]; Mozambique National Resistance-Electoral Union (Resistencia Nacional Mocambicana-Uniao Eleitoral) or RENAMO-UE [Afonso DHLAKAMA, president] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Institute for Peace and Democracy (Instituto para Paz e Democracia) or IPADE [Raul DOMINGOS, president]; Etica [Abdul CARIMO Issa, chairman]; Movement for Peace and Citizenship (Movimento para Paz e Cidadania); Mozambican League of Human Rights (Liga Mocambicana dos Direitos Humanos) or LDH [Alice MABOTE, president]; Human Rights and Development (Direitos Humanos e Desenvolvimento) or DHD [Artemisia FRANCO, secretary general] |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OIC, ONUB, OPCW, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISET, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Armando PANGUENE
chancery: 1990 M Street NW, Suite 570, Washington, DC 20036 telephone: [1] (202) 293-7146 FAX: [1] (202) 835-0245 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Helen LA LIME
embassy: Avenida Kenneth Kuanda 193, Maputo mailing address: P. O. Box 783, Maputo telephone: [258] (1) 492797 FAX: [258] (1) 490448 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), black, and yellow with a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; the black band is edged in white; centered in the triangle is a yellow five-pointed star bearing a crossed rifle and hoe in black superimposed on an open white book |
| Economy | Mozambique |
|
Economy - overview:
|
At independence in 1975, Mozambique was one of the world's poorest countries. Socialist mismanagement and a brutal civil war from 1977-92 exacerbated the situation. In 1987, the government embarked on a series of macroeconomic reforms designed to stabilize the economy. These steps, combined with donor assistance and with political stability since the multi-party elections in 1994, have led to dramatic improvements in the country's growth rate. Inflation was reduced to single digits during the late 1990s although it returned to double digits in 2000-03. Fiscal reforms, including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities. In spite of these gains, Mozambique remains dependent upon foreign assistance for much of its annual budget, and the majority of the population remains below the poverty line. Subsistence agriculture continues to employ the vast majority of the country's workforce. A substantial trade imbalance persists although the opening of the MOZAL aluminum smelter, the country's largest foreign investment project to date has increased export earnings. Additional investment projects in titanium extraction and processing and garment manufacturing should further close the import/export gap. Mozambique's once substantial foreign debt has been reduced through forgiveness and rescheduling under the IMF's Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and Enhanced HIPC initiatives, and is now at a manageable level. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $23.38 billion (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
8.2% (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $1,200 (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 21.1%
industry: 32.1% services: 46.9% (2004 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
9.2 million (2000 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 81%, industry 6%, services 13% (1997 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
21% (1997 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
70% (2001 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2.5%
highest 10%: 31.7% (1997) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
39.6 (1996-97) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
12.8% (2004 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
47% of GDP (2004 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $1.186 billion
expenditures: $1.398 billion, including capital expenditures of $479.4 million (2004 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
cotton, cashew nuts, sugarcane, tea, cassava (tapioca), corn, coconuts, sisal, citrus and tropical fruits, potatoes, sunflowers; beef, poultry |
|
Industries:
|
food, beverages, chemicals (fertilizer, soap, paints), aluminum, petroleum products, textiles, cement, glass, asbestos, tobacco |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
3.4% (2000) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
8.859 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 2.9%
hydro: 97.1% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
5.046 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
7.1 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
3.907 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
8,500 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
0 bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
60 million cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
60 million cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
63.71 billion cu m (1 January 2002) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$-101.2 million (2004 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$689.4 million f.o.b. (2004 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
aluminum, prawns, cashews, cotton, sugar, citrus, timber; bulk electricity |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Belgium 32%, Italy 13.9%, Spain 12.6%, Germany 9.8%, Zimbabwe 4.7% (2004) |
|
Imports:
|
$972.9 million f.o.b. (2004 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and equipment, vehicles, fuel, chemicals, metal products, foodstuffs, textiles |
|
Imports - partners:
|
South Africa 35.7%, Australia 10.9%, US 3.7% (2004) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$1.206 billion (2004 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$966 million (2002 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$632.8 million (2001) |
|
Currency (code):
|
metical (MZM) |
|
Currency code:
|
MZM |
|
Exchange rates:
|
meticais per US dollar - 22,581 (2004), 23,782 (2003), 23,678 (2002), 20,704 (2001), 15,227 (2000)
note: effective October 2000, the exchange rate is determined as the weighted average of buying and selling exchange rates of all transactions of commercial banks and stock exchanges with the public |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Mozambique |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
83,700 (2002) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
428,900 (2003) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: fair system but not available generally (telephone density is only 16 telephones for each 1,000 persons)
domestic: the system consists of open-wire lines and trunk connection by microwave radio relay and tropospheric scatter international: country code - 258; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (2 Atlantic Ocean and 3 Indian Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 13, FM 17, shortwave 11 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
730,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
1 (2001) |
|
Televisions:
|
67,600 (2000) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.mz |
|
Internet hosts:
|
3,249 (2003) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
11 (2002) |
|
Internet users:
|
50,000 (2002) |
| Transportation | Mozambique |
|
Railways:
|
total: 3,123 km
narrow gauge: 2,983 km 1.067-m gauge; 140 km 0.762-m gauge (2004) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 30,400 km
paved: 5,685 km unpaved: 24,715 km (1999 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
460 km (Zambezi River navigable to Tete and along Cahora Bassa Lake) (2004) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 649 km; refined products 292 km (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Beira, Maputo, Nacala |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 2 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 4,125 GRT/7,024 DWT
by type: cargo 2 foreign-owned: 2 (Belgium 2) (2005) |
|
Airports:
|
158 (2004 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 22
over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 3 1,524 to 2,437 m: 10 914 to 1,523 m: 3 under 914 m: 5 (2004 est.) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 136
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 14 914 to 1,523 m: 34 under 914 m: 87 (2004 est.) |
| Military | Mozambique |
|
Military branches:
|
Mozambique Armed Defense Forces: Army, Navy, Air and Air Defense Forces, Logistics Command |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 18-49: 3,793,373 (2005 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 1,751,223 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$117.3 million (2004) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
2.2% (2004) |
| Transnational Issues | Mozambique |
|
Disputes - international:
|
none |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
Southern African transit point for South Asian hashish and heroin, and South American cocaine probably destined for the European and South African markets; producer of cannabis (for local consumption) and methaqualone (for export to South Africa); corruption and poor regulatory capability makes the banking system vulnerable to money laundering, but the lack of a well-developed financial infrastructure limits the country's utility as a money-laundering center |
|
This page was last updated on 20 September, 2005 |