

| The World Factbook | ||


|
Bahamas, The |

|
|
| Introduction | Bahamas, The |
|
Background:
|
Arawak Indians inhabited the islands when Christopher Columbus first set foot in the New World on San Salvador in 1492. British settlement of the islands began in 1647; the islands became a colony in 1783. Since attaining independence from the UK in 1973, The Bahamas have prospered through tourism and international banking and investment management. Because of its geography, the country is a major transshipment point for illegal drugs, particularly shipments to the US, and its territory is used for smuggling illegal migrants into the US. |
| Geography | Bahamas, The |
|
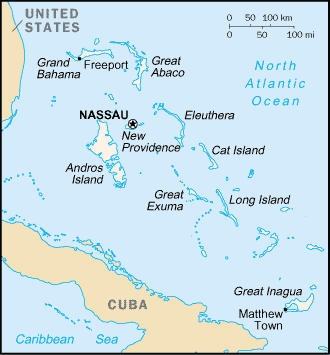
Location:
|
Caribbean, chain of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida, northeast of Cuba |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
24 15 N, 76 00 W |
|
Map references:
|
Central America and the Caribbean |
|
Area:
|
total: 13,940 sq km
land: 10,070 sq km water: 3,870 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Connecticut |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
3,542 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
tropical marine; moderated by warm waters of Gulf Stream |
|
Terrain:
|
long, flat coral formations with some low rounded hills |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Alvernia, on Cat Island 63 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
salt, aragonite, timber, arable land |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0.8%
permanent crops: 0.4% other: 98.8% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
NA |
|
Natural hazards:
|
hurricanes and other tropical storms cause extensive flood and wind damage |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
coral reef decay; solid waste disposal |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location adjacent to US and Cuba; extensive island chain of which 30 are inhabited |
| People | Bahamas, The |
|
Population:
|
301,790
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2005 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 27.9% (male 42,142/female 42,096)
15-64 years: 65.9% (male 97,865/female 101,047) 65 years and over: 6.2% (male 7,616/female 11,024) (2005 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 27.55 years
male: 26.78 years female: 28.34 years (2005 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.67% (2005 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
17.87 births/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
8.97 deaths/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-2.18 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2005 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/female total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2005 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 25.21 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 31.02 deaths/1,000 live births female: 19.28 deaths/1,000 live births (2005 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 65.54 years
male: 62.11 years female: 69.04 years (2005 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.2 children born/woman (2005 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
3% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
5,600 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
less than 200 (2003 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Bahamian(s)
adjective: Bahamian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
black 85%, white 12%, Asian and Hispanic 3% |
|
Religions:
|
Baptist 35.4%, Anglican 15.1%, Roman Catholic 13.5%, Pentecostal 8.1%, Church of God 4.8%, Methodist 4.2%, other Christian 15.2%, none or unspecified 2.9%, other 0.8% (2000 census) |
|
Languages:
|
English (official), Creole (among Haitian immigrants) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 95.6% male: 94.7% female: 96.5% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Bahamas, The |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Commonwealth of The Bahamas
conventional short form: The Bahamas |
|
Government type:
|
constitutional parliamentary democracy |
|
Capital:
|
Nassau |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
21 districts; Acklins and Crooked Islands, Bimini, Cat Island, Exuma, Freeport, Fresh Creek, Governor's Harbour, Green Turtle Cay, Harbour Island, High Rock, Inagua, Kemps Bay, Long Island, Marsh Harbour, Mayaguana, New Providence, Nichollstown and Berry Islands, Ragged Island, Rock Sound, Sandy Point, San Salvador and Rum Cay |
|
Independence:
|
10 July 1973 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 10 July (1973) |
|
Constitution:
|
10 July 1973 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English common law |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952), represented by Governor General Dame Ivy DUMONT (since NA May 2002)
head of government: Prime Minister Perry CHRISTIE (since 3 May 2002) and Deputy Prime Minister Cynthia PRATT (since 7 May 2002) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on the prime minister's recommendation elections: none; the monarch is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition is usually appointed prime minister by the governor general; the prime minister recommends the deputy prime minister |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (16-member body appointed by the governor general upon the advice of the prime minister and the opposition leader for five-year terms) and the House of Assembly (40 seats; members elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms); the government may dissolve the parliament and call elections at any time
elections: last held 1 May 2002 (next to be held by May 2007) election results: percent of vote by party - PLP 50.8%, FNM 41.1%, independents 5.2%; seats by party - PLP 29, FNM 7, independents 4 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court; Court of Appeal; magistrates courts |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Free National Movement or FNM [Tommy TURNQUEST]; Progressive Liberal Party or PLP [Perry CHRISTIE] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, C, Caricom, CDB, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICFTU, ICRM, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOM, IOC, ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW (signatory), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer) |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Joshua SEARS
chancery: 2220 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 319-2660 FAX: [1] (202) 319-2668 consulate(s) general: Miami and New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador John D. ROOD
embassy: 42 Queen Street, Nassau mailing address: local or express mail address: P. O. Box N-8197, Nassau; Department of State, 3370 Nassau Place, Washington, DC 20521-3370 telephone: [1] (242) 322-1181, 328-2206 (after hours) FAX: [1] (242) 356-0222 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of aquamarine (top), gold, and aquamarine, with a black equilateral triangle based on the hoist side |
| Economy | Bahamas, The |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The Bahamas is a stable, developing nation with an economy heavily dependent on tourism and offshore banking. Tourism alone accounts for more than 60% of GDP and directly or indirectly employs half of the archipelago's labor force. Steady growth in tourism receipts and a boom in construction of new hotels, resorts, and residences had led to solid GDP growth in recent years, but the slowdown in the US economy and the attacks of 11 September 2001 held back growth in these sectors in 2001-03. Financial services constitute the second-most important sector of the Bahamian economy, accounting for about 15% of GDP. However, since December 2000, when the government enacted new regulations on the financial sector, many international businesses have left The Bahamas. Manufacturing and agriculture together contribute approximately a tenth of GDP and show little growth, despite government incentives aimed at those sectors. Overall growth prospects in the short run rest heavily on the fortunes of the tourism sector, which depends on growth in the US, the source of more than 80% of the visitors. In addition to tourism and banking, the government supports the development of a "third pillar," e-commerce. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $5.295 billion (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
3% (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $17,700 (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 3%
industry: 7% services: 90% (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
156,000 (1999) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 5%, industry 5%, tourism 50%, other services 40% (1999 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
10.2% (2004 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: 27% (2000) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
1.2% (year ending September 2004) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $1 billion
expenditures: $1 billion, including capital expenditures of $106.7 million (FY03/04) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
citrus, vegetables; poultry |
|
Industries:
|
tourism, banking, cement, oil transshipment, salt, rum, aragonite, pharmaceuticals, spiral-welded steel pipe |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA |
|
Electricity - production:
|
1.716 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
1.596 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2002) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
23,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
transhipments of 29,000 bbl/day (2003) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA |
|
Exports:
|
$636 million (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
mineral products and salt, animal products, rum, chemicals; fruit and vegetables |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 42.1%, Spain 10.3%, Poland 6.1%, Germany 6.1%, Switzerland 4.9%, Paraguay 4.8%, France 4.5%, Mexico 4.5% (2004) |
|
Imports:
|
$1.63 billion (2003) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment, manufactures, chemicals, mineral fuels; food and live animals |
|
Imports - partners:
|
US 22.3%, South Korea 19%, Japan 8.2%, Brazil 8.2%, Italy 8.1%, Venezuela 6.8% (2004) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$308.5 million (2002) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$9.8 million (1995) |
|
Currency (code):
|
Bahamian dollar (BSD) |
|
Currency code:
|
BSD |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Bahamian dollars per US dollar - 1 (2004), 1 (2003), 1 (2002), 1 (2001), 1 (2000) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June |
| Communications | Bahamas, The |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
131,700 (2003) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
121,800 (2002) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: modern facilities
domestic: totally automatic system; highly developed international: country code - 1-242; tropospheric scatter and submarine cable to Florida; 3 coaxial submarine cables; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (1997) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 3, FM 5, shortwave 0 (2004) |
|
Radios:
|
215,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
2 (2004) |
|
Televisions:
|
67,000 (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.bs |
|
Internet hosts:
|
302 (2003) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
19 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
84,000 (2003) |
| Transportation | Bahamas, The |
|
Highways:
|
total: 2,693 km
paved: 1,546 km unpaved: 1,147 km (1999 est.) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Freeport, Nassau, South Riding Point |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 1,119
by type: barge carrier 2, bulk carrier 183, cargo 259, chemical tanker 54, combination ore/oil 17, container 74, liquefied gas 28, livestock carrier 2, passenger 116, passenger/cargo 40, petroleum tanker 168, refrigerated cargo 130, roll on/roll off 20, specialized tanker 2, vehicle carrier 24 foreign-owned: 968 (Angola 4, Australia 4, Belgium 17, Canada 9, China 3, Croatia 1, Cuba 1, Cyprus 13, Denmark 18, Estonia 1, Finland 7, France 28, Germany 15, Greece 194, Hong Kong 11, Indonesia 2, Ireland 1, Israel 1, Italy 7, Japan 49, Jordan 2, Kenya 1, Latvia 1, Malaysia 12, Monaco 15, Netherlands 24, New Zealand 1, Nigeria 2, Norway 229, Poland 13, Reunion 1, Russia 2, Saudi Arabia 12, Serbia & Montenegro 2, Singapore 11, Slovenia 1, South Korea 1, Spain 6, Sweden 9, Switzerland 4, Thailand 1, Trinidad & Tobago 2, Turkey 7, UAE 12, United Kingdom 55, United States 154, Uruguay 2) registered in other countries: 35 (2005) |
|
Airports:
|
63 (2004 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 29
over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 3 1,524 to 2,437 m: 14 914 to 1,523 m: 9 under 914 m: 1 (2004 est.) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 34
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 10 under 914 m: 21 (2004 est.) |
|
Heliports:
|
1 (2004 est.) |
| Military | Bahamas, The |
|
Military branches:
|
Royal Bahamaian Defense Force (naval forces) (2004) |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
18 years of age (est.); no conscription (2001) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
NA |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
NA |
| Transnational Issues | Bahamas, The |
|
Disputes - international:
|
have not been able to agree on the alignment of a maritime boundary with the US; continues to monitor and interdict Haitian refugees fleeing economic privation and political instability |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
transshipment point for cocaine and marijuana bound for US and Europe; offshore financial center |
|
This page was last updated on 20 September, 2005 |