Dynamics of fluids: Pressure and Pascal's principle.

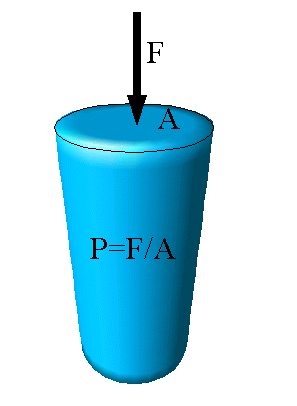
Pressure
In general, pressure exerted on one object is
defined as the ratio
between the perpendicular force applied
to the object's surface and the area of the involved surface.
The unit of measurement in the SI system is called Pascal (Pa). One
Pascal equals one Newton per meter squared.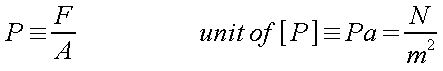
Pascal's principle
Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) discovered
that in a fluid, any pressure applied insists uniformly in all the
direction of the fluid , and any change in pressure is transmitted
identically throughout it. For instance, all the hydraulic devices
take advantage from the principle in order to obtain larger forces
starting from a small force applied. (See the description of how
hydraulic jacks work in the textbook on page 161).
 Atmospheric
pressure
Atmospheric
pressure
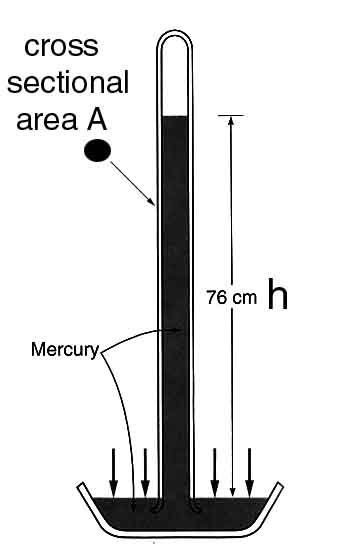
Atmospheric pressure at a given height from the sea
level is the pressure due to the weight of atmosphere insisting at
that height. Evangelista Torricelli (1608-1647) demonstrated that
atmospheric pressure at sea level can support a column of mercury 76
cm in height; in other words, air pressure at sea level balances
exactly the weight of such a column. Hence, by knowing the density of
mercury, the evaluation of the atmospheric pressure at sea level is a
simple matter. If the column of mercury is contained in a tube with a
cross sectional area A atmospheric pressure is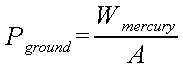
Since
the density of a substance is defined as the ratio between its mass
and its volume:
the
pressure will be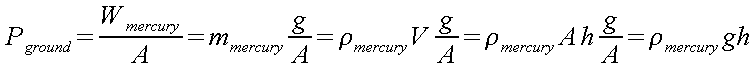
where
“h” is the height of the column, “g” is the
acceleration of gravity, “![]() ”
the density of mercury whose value can be read in following table:
”
the density of mercury whose value can be read in following table:
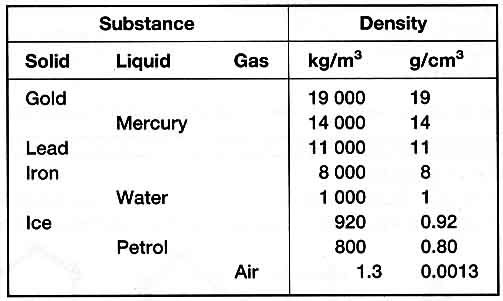
hence
the evaluation yields to:
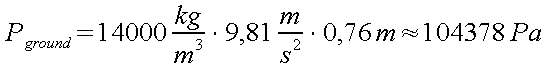
that
means atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 100
kilopascal.
As we go up from sea level, there is less atmosphere
above us, and the pressure decrease. However atmospheric pressure
depends not only from the height from the ground, but also from the
changes in the weather, Pascal observed that columns height were
lower on stormy days and higher on clear days. This pressure
variation is actually used to indicate and to forecast weather
conditions.