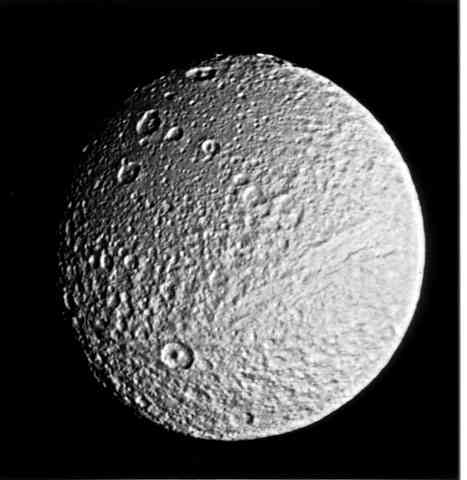

This Voyager 2 photograph of Tethys shows objects
about 5 kilometers (3 miles) in size and is one of the best images
of the Saturnian satellite returned by the spacecraft or its predecessor,
Voyager 1. Voyager 2 obtained this picture Aug. 26 from a range
of 282,000 kilometers (175,000 miles). It has been specially processed
by computer to bring out fine detail on the surface. A boundary
between heavily cratered regions (top right) and more lightly
cratered areas (bottom right) is very similar to boundaries on
the moons Dione and Rhea, indicating a period of internal activity
early in Tethys' history that partially resurfaced the older terrain.
The large crater in the upper right lies almost on the huge trench
system that girdles nearly three-fourths of the circumference
of the satellite. The trench itself is seen in this image as a
linear set of markings to the lower left of the crater. The trench,
several kilometers deep, is indicative of a cold, stiff ice crust
at the time of its formation. Formation of this trench system
could have resulted from the expansion of Tethys as its warm interior
froze. The Voyager project is managed for NASA by the Jet Propulsion
Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. (P-24065)