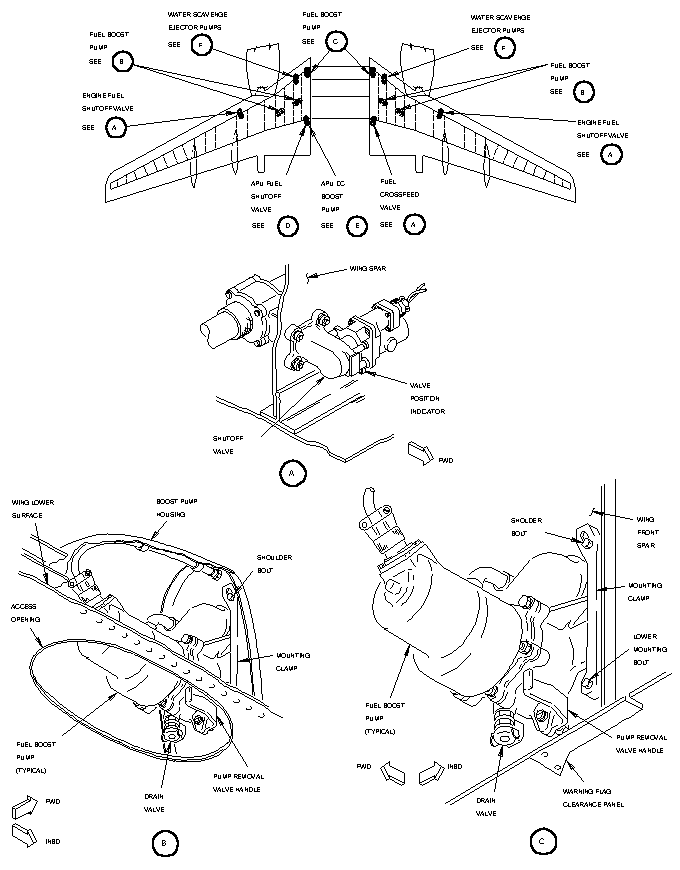
A.The fuel feed system supplies fuel to the engines and APU from the fuel tanks. For ground operations only, the system can be used for transferring fuel from one tank to another or for defueling the tanks.
B.The fuel feed system consists of two boost pumps in each tank, a check valve downstream of each boost pump, a boost pump removal valve for each boost pump, a boost pump bypass valve for tanks No. 1 and 2, an engine fuel shutoff valve for each engine, a fuel crossfeed valve, and an APU fuel valve.
C.The fuel control panel, on pilot's overhead panel, contains the controls and indicators for the fuel feed system. They are a boost pump control switch and low pressure indicating light for each boost pump, a fuel shutoff valve position indicating light, filter bypass lights, a fuel temperature indicator, and a fuel crossfeed valve switch and position indicating light.
D.Power for the boost pumps is 115v ac. The APU fuel, engine shutoff and crossfeed valves require 28v dc power.

2.Engine Fuel Shutoff Valve
A.Two engine fuel shutoff valves mounted on the wing front spar provide the means of shutting off the fuel supply to the engines. Each valve is an electric motor-driven slide shutoff valve with a manual override handle. The manual override handle provides a visual check of the valve position and a manual method of positioning the valve when the electric motor is not energized. To limit the pressure buildup in the fuel lines, the valve housing incorporates a thermal relief valve.
B.The valves are operated by 28-volt dc power and are controlled by the fire switches on the aft electronics panel and through a mechanically operated switch on the aisle stand. Whenever the engine start lever is in the cutoff position the mechanically operated switch is actuated to close the shutoff valve. The engine fuel shutoff valve position light is illuminated bright when valve is in transit. It is dim when valve is closed and extinguished when valve is open.
3.Fuel Crossfeed Valve
A.The engine fuel feed lines are connected by use of the crossfeed valve. It provides the means of directing fuel to both engines from any tank. The valve is located on the rear spar of tank No. 2. It is the same design as the engine fuel shutoff valve.
B.The crossfeed valve position light is illuminated bright while valve is in transit. It is dim when valve is open and extinguished when valve is closed.
4.Fuel Boost Pump
A.The fuel boost pumps deliver fuel under pressure from a tank to its respective engine or through the crossfeed valve to the other engine. Each pump is a centrifugal-type pump driven by an ac motor controlled by a separate switch on the overhead panel. Each pump is isolated from the fuel tank by being installed in a pump housing within a tank or on the forward side of the front spar.
B.Fuel enters the pump through a wire mesh screen at the suction tube inlet then flows through a manually operated pump removal valve. The pump removal valve allows removal of a pump without draining the tank. A portion of the fuel being pumped is circulated through the pump to act as a lubricant for the bearings and a coolant for the motor. Fuel is discharged from the pump through the boost pump check valve. A small vent valve vents the pump casing to the fuel tank. Boost pump reprime lines prime center tank boost pumps whenever center tank is refueled.
C.The low pressure lights for the boost pumps will come on if the boost pump pressure is low and the pump switch is ON. For the boost pumps in the No. 1 tank and No. 2 tank, the low pressure lights will come on if the boost pump switch is OFF. For the boost pumps in the center tank, the low pressure lights are off if the boost pump switch is OFF. Thus, no low pressure lights are on during the usual part of the flight when the center tank is empty and the boost pumps in the center tank do not operate.
5.Fuel Boost Pump Check Valve
A.The fuel boost pump check valve closes the boost pump outlet line when the pressure drops below a predetermined amount, thus preventing reverse fuel flow to the boost pump. Main tank boost pump check valves differ from center tank boost pump check valves as the cracking pressure for main tank boost pump check valves is approximately 12 psi and cracking pressure for center wing tank boost check valves is approximately 1.3 psi. The valve consists of a spring-loaded-closed flapper valve mounted in a housing. The housing has three ports: fuel in, fuel out and a pressure sensing port. The pressure sensing port is located upstream of the flapper valve and is connected to the boost pump low pressure switch. The valves are located inside the fuel tank on the wall of the boost pump housing.
6.Fuel Boost Pump Removal Valve
A.The fuel boost pump removal valve permits removing the fuel boost pump without defueling the tank. The valves are manually operated slide shutoff valves and are located in the inlet line to each fuel boost pump. The valve control shaft passes through the wall of the boost pump housing so that the valve may be operated from the outside of the fuel tank.
7.Fuel Boost Pump Bypass Valve
A.A boost pump bypass valve allows the engines to draw fuel from tank No. 1 or 2 by suction in case of complete boost pump failure in that tank. The valve also allows defueling the tanks by suction through the manually- operated defueling valve.
B.Boost pump bypass valves are located at the inboard end of tanks No. 1 and No. 2. Valves are not installed in the center tank.
C.One of two types of bypass valves is installed in the airplane: either a flapper-type check valve contained within the suction inlet screen assembly, or a separate check valve installed in-line between the inlet screen and the crossfeed manifold. The separate check valve is the preferred installation as the valve contained within the suction inlet screen is susceptible to water accumulation and possible freezing in the closed position.
D.With boost pump pressure applied, the bypass valve will be closed, preventing fuel in the fuel manifold from re-entering the fuel tank. With suction applied, the bypass valve will be open, allowing the engine to draw fuel from the tank.
8.APU Fuel Shutoff Valve
A.The APU fuel valve is mounted on the left wing rear spar and controls delivery of fuel from tank No. 1 to the APU. The valve is an electric motor-driven rotary gate valve with a manual override handle. The manual override handle provides a visual check of the valve position and a manual method of positioning the valve when the electric motor is not energized. To limit pressure buildup in the fuel lines, the valve housing incorporates a thermal relief valve. The valve is operated by 28 volt dc power and is controlled by the APU master switch.
9.APU DC Boost Pump
A.The APU dc boost pump supplies fuel under pressure from tank No. 1 to the APU fuel feed line as necessary for cold starting or after air has entered the fuel feed line.
B.The boost pump is mounted on the left lower inboard trailing edge panel and pumps fuel through tube lines which penetrate the left wing rear spar. The pump operates on 28-volt dc power and will run for approximately 1 minute during APU ground or in-flight starting.
10.Fuel Lines and Couplings
A.The lines that transfer fuel from the tanks to the engine are fabricated from seamless aluminum alloy tubing, and are connected to the various fuel system components by standard unions, couplings or flanges. Bonding jumpers are used to ensure positive electrical grounding of the tubing and fittings to the airplane structure. The lines in the wings are mainly located inside the fuel tank boundaries.
B.The APU fuel line segment from the center tank fitting to the bulkhead connection on the APU shroud is mainly a flexible hose enclosed in a metal fuel line shroud. The fuel line continues from the APU shroud to the APU fuel control but is not separately shrouded for this distance.
11.Water Scavenge Ejector Pump
A.Two ejector pumps located on the wing front spar adjacent to the forward fuel boost pump provide continuous water scavenging whenever the forward boost pumps are operating. The pump consists of a housing, a jet nozzle, and a spring-loaded flapper valve. The housing has three ports: a motive flow port, an induced flow port, and a discharge port. The motive port is connected to an adapter plate between the forward boost pump and the check valve. The induced port is connected to an inlet located in the low area of the fuel tank. The discharge port is connected to a line which is open to the boost pump inlet. The spring-loaded flapper valve closes when the jet nozzle is removed to allow nozzle removal without defueling the tank.
B.When the forward boost pump is operating, it pressurizes the motive port of each ejector pump. Flow through the jet nozzle causes fuel and accumulated water to flow from the inlet into the induced port and out the discharge port.
12.Operation
A.The engine fuel feed system will supply fuel to the engines by a direct tank-to-engine feed or from any tank to either or both engines through the crossfeed valve when the boost pumps are operating. To obtain direct tank-to-engine feed, the fuel crossfeed valve is closed, the engine fuel shutoff valves are opened. For crossfeed, the fuel crossfeed valve and the engine fuel shutoff valves are opened and the applicable boost pumps are operated.
B.The engine fuel shutoff and crossfeed valves are operated by 28 volt dc motors. Control of the crossfeed valve is by a switch on fuel system module (P5 panel). The engine fuel shutoff valves will close when the fire switches are placed in FIRE position. Normal shutoff valve control is with the engine start lever (in cutoff, valve is closed; in idle, valve is open).
C.The center tank boost pumps override tanks No. 1 and 2 boost pumps since pressure from tanks No. 1 and 2 tank boost pumps has to overcome a boost pump check valve cracking pressure of 12 psi, while center tank boost pumps have only a 1.3 psi check valve cracking pressure to overcome.
D.The APU fuel valve is controlled by the APU master switch. The APU fuel valve is closed when an APU fire switch is energized.
E.A boost pump bypass valve in tanks No. 1 and 2 allows suction fuel feed if boost pump pressure is lost.