In this section will be taken into examen the common topologies used for the rectifying functions. Audio designers involved in tubed-amp designs can benefit of many choices based on solid state, vacuum tube and hybrid solutions. The results are presented in synthetic form for a quick evaluation. At the end three summary table are presented.
Test Conditions:
Parameters under Evaluation
SS Wheastone's Bridge
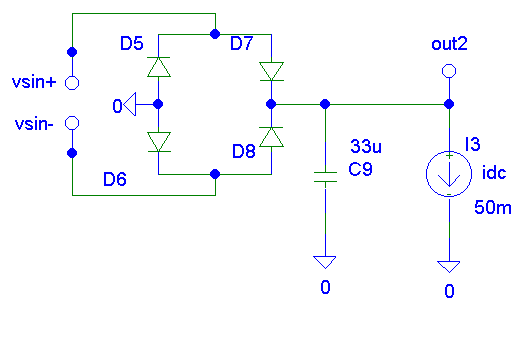
VCE = 1.36
Ripple = 13.61Vpp
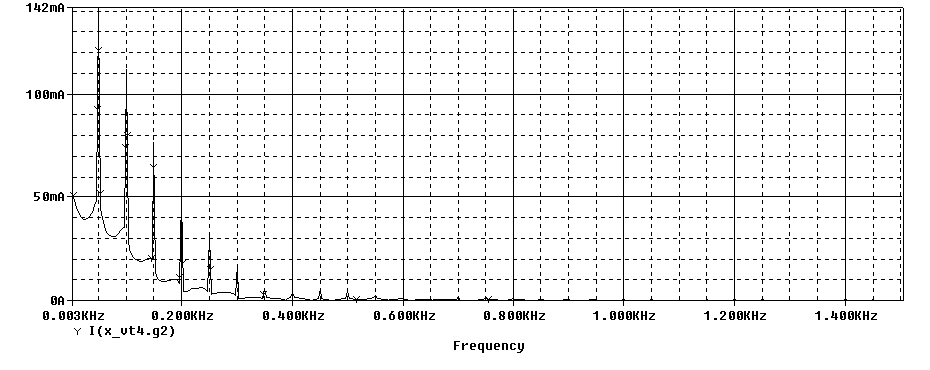
Diode's Pulse Current FFT

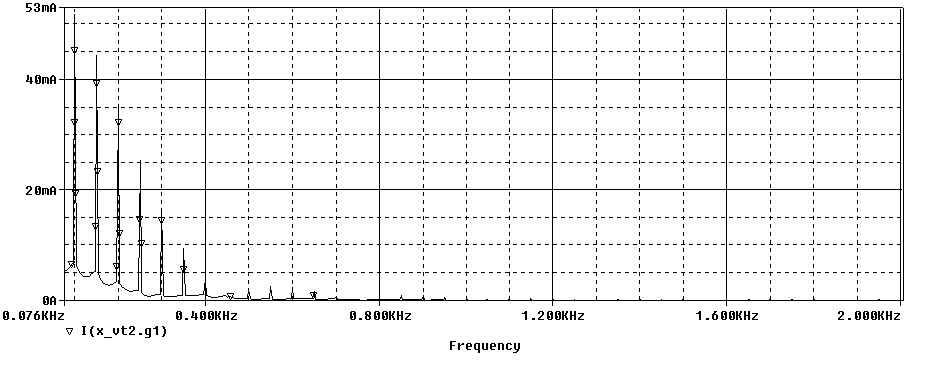
VT Wheastone's Bridge (3 Tubes)
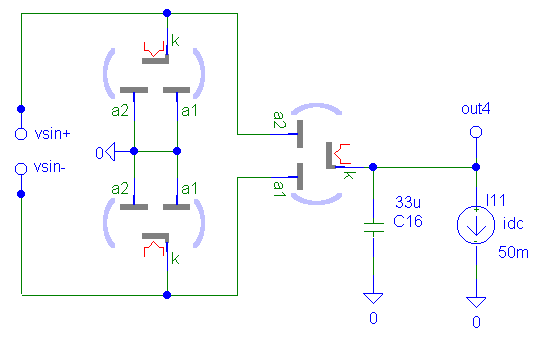
VCE = 1.07
Ripple = 24.47Vpp
Diode's Pulse Current FFT
VT Wheastone's Bridge (4 Tubes)
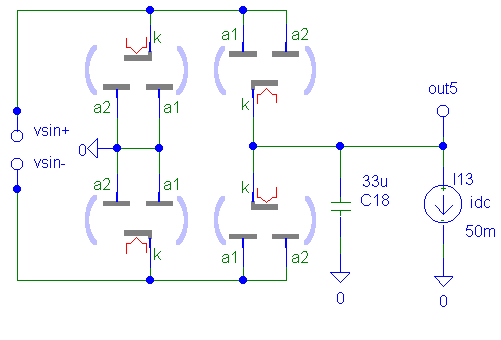
VCE = 1.24
Ripple = 11.148Vpp
Diode's Pulse Current FFT

"Classical" VT Rectifying Circuit

VCE = 1.17
Ripple = 10.45Vpp
Diode's Pulse Current FFT
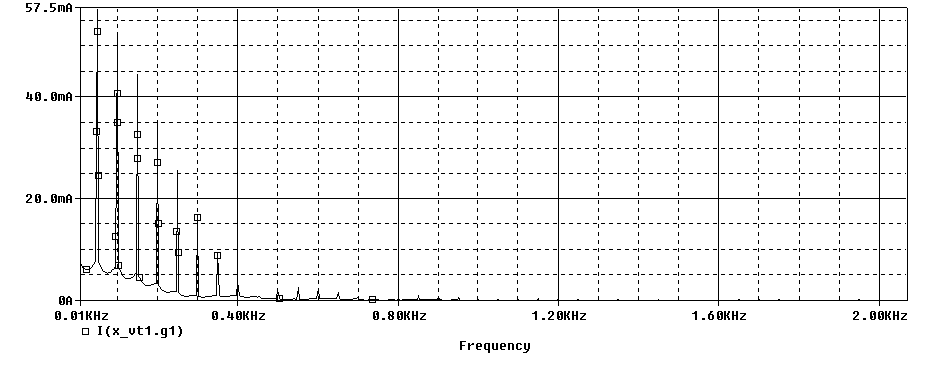
Hybrid Bridge ![]()

VCE = 1.36
Ripple = 13.61Vpp
Diode's Pulse Current FFT
Summary
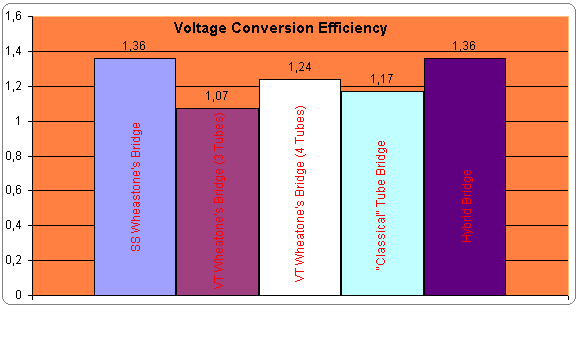
Fig. 1 VCE for the examined circuits
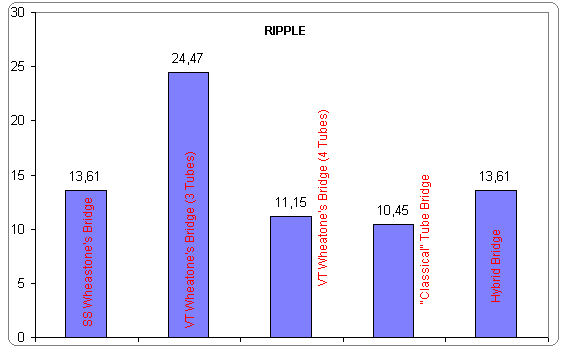
Fig.2 Ripple values
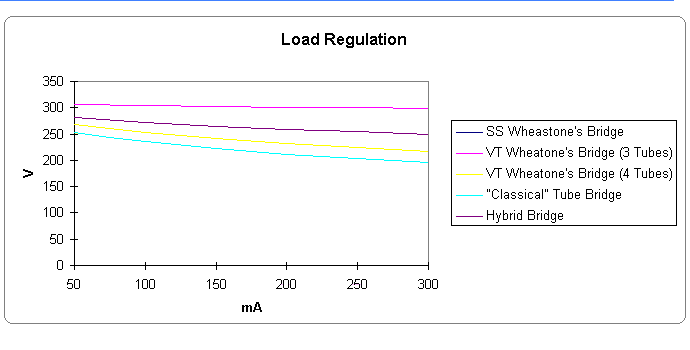
Fig. 3 Load capabilites of different topologies
Conclusions
The hybrid bridge results in the best trade-off between electrical and sonical requirements. This wonderful topology keep off also the requirement of a center-tapped power transformer and permits the easy solid-state-like production of a contemporary positive and negative rail. On the contrary pulse current FFTs have the vacuum-tube imprint.
|
What did you
think of this article? |