THE PLAGUE - POSTEXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS - THERAPY
The Plague. The data reported from the WHO refer the presence of approximately 1000/3000 cases the year plague, distributed above all between Africa, South America and Asia. In the United States the last city epidemic of plague has been taken place in 1924-25, to Los Angeles, and from then the manifest disease in particolar way in the rural areas with a 10-15 rhythm cases the year, above all in the zone of the New Mexico, Arizona north and south Colorado, and in the zone comprised between California, the south of the Oregon and western Nevada. In Asia the plague is diffused in the zones of the Caucasus. Present also in Russia, in China, and also in some zones of south-western and Southeastern Asia. The plague is present in Uganda (November 1988, 49 cases), Malawi (July 1999, 74 cases), Namibia (May 1999, 39 cases) in Madagascar and Sudafrica. The plague is instead absent in Europe and Australia. To recognize the plague it is important to understand the presentation of disease.
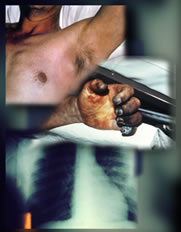
Bubonic Plague: incubation period is 2-6 days. Early symptoms are lymphadenopathy and fever. Patients develop swollen lymph nodes, which are called buboes. If bubonic plague is not treated, the bacteria can scatter through the bloodstream causing septicemia or infect the lungs.
Pneumonic Plague: incubation period is 2-4 days with range of 1- 6 days. Symptoms are acute attack of fever, myalgias associated with progressive lack of energy. It is caused by direct inhalation of infective respiratory droplets or aerosolized bacteria. Chest radiographs of untreated patients show rapidly expanding bronchopneumonic infiltrates. Without early diagnosis and therapy in less than 24 hours, pneumonic plague is generally fatal.
Septicemic Plague is frequently fatal also when treated. Occurs when Yersinia Pestis increase in the blood. Symptoms are acute attack of fever, prostration,vomit,nausea, abdominal pain,purpura. Subsequently the disease may develop disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
POSTEXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
Doxycycline is the first choice antibiotic for postexposure prophylaxis. Once plague is suspected or confirmed in a particular region, anyone in that region with fever of 38.5°C or higher, with cough, shortly should be treated with antimicrobic for plausible pneumonic plague. Asymptomatic persons who have had contact with persons with untreated pneumonic plague should receive postexposure prophylaxis for 7 days and should be observed consequently for fever and cough. Antimicrobic recommended for these individuals: tetracycline, doxycycline, sulfonamides and chloramphenicol.
THERAPY
Adults Preferred choices: Streptomycin, 1g IM twice daily; Gentamicin, 5 mg/kg IM or IV once daily or 2 mg/kg loading dose followed by 1.7 mg/kg IM or IV three times daily. Alternative choices: Doxycycline, 100 mg IV twice daily or 200 mg IV once daily; Ciprofloxacin, 400 mg IV twice daily; Chloramphenicol, 25 mg/kg IV 4 times daily.
Children Preferred choices: Streptomycin, 15 mg/kg IM twice daily (maximum daily dose 2 g); Gentamicin, 2.5 mg/kg IM or IV 3 times daily. Alternative choices: Doxycycline, If >= 45 kg, give adult dosage If < 45 kg, give 2.2 mg/kg IV twice daily (maximum 200 mg/dl); Ciprofloxacin, 15 mg/kg IV twice daily; Chloramphenicol, 25 mg/kg IV 4 times daily.
Pregnant Women Preferred choice: Gentamicin, 5 mg/kg IM or IV once daily or 2 mg/kg loading dose followed by 1.7 mg/kg IM or IV three times daily. Alternative choices: Doxycycline, 100 mg IV twice daily or 200 mg IV once daily Ciprofloxacin, 400 mg IV twice daily.
Postexposure Prophylaxis
Adults Preferred choices: Doxycycline, 100 mg orally twice daily; Ciprofloxacin, 500 mg orally twice daily Alternative choices: Chloramphenicol, 25 mg/kg orally 4 times daily
Children Preferred choices: Doxycycline, If >=45kg give adult dosage If <45 kg then give 2.2 mg/kg orally twice daily Ciprofloxacin, 20 mg/kg orally twice daily Alternative choices: Chloramphenicol, 25 mg/kg orally 4 times daily
Pregnant Women Preferred choices: Doxycycline, 100 mg orally twice daily and Ciprofloxacin, 500 mg orally twice daily Alternative choices: Chloramphenicol, 25 mg/kg orally 4 times daily